Linear ball bearings / block form / aluminium / anodised / double bushing (LHSSWF6)
- Volume Discount
Product Details:
Manufacturer part number: LHSSWF6
Brand: MISUMI
Price: 22.43 €
Delivery time: 5 Days
Technical Data:
[dr] Inner Diameter: 6 mm
[L] Length (Total): 46 mm
Material of Outer Cylinder: [Steel] EN 1.3505 Equiv.
[D] Outer Diameter: 12 mm
Basic Load Rating Dynamic Rating (Detail): 324 N
- Order quantities extended (D-JIT)
- Stock
Part Number
Once your search is narrowed to one product,
the corresponding part number is displayed here.
LHSSWF6
- Drawing / Specifications
- 3D Preview 3D preview is available after complete configuration
- Part Numbers
- More Information
- Catalog
- Technical Information
Back to the Category Linear Ball Bushings
| Type | Linear Bushing Used | Housing | Ambient Operating Temp. | |||
| (Here) | (Here) | |||||
| Standard | Compact | Standard | Compact | Material | Surface Treatment | |
| LHSSW | LHSSKW | LMU | LMK | Aluminum Alloy | Clear Anodize | -20~ 80°C |
| LHSSWF | - | LMUF | - | -20~110°C | ||
| SLHSSW | - | SLMU | - | -20~ 80°C | ||
| SLHSSWF | - | SLMUS | - | -20~110°C | ||
Further specifications can be found under the tab More Information.
Details on lubricants can be found in the catalog on p. 304
| Part Number | |
LHSSW12 LHSSW12L LHSSW12L LHSSW12G LHSSW12G LHSSW12H LHSSW12H | (L Type Greased) (G Type Greased) (H Type Greased) |
For Days to Ship, Price and Performance, see. >> P.304
Linear Ball Bushing Selection Details
- Inner diameter [dr]: 3 mm – 100 mm
- Total length [L]: 10 mm – 300 mm
- Housing material: aluminum, stainless steel (stainless steel), steel
- Ball material: stainless steel (stainless steel), steel
- Ball cage material: plastic, stainless steel (stainless steel)
- Surface treatment: without, chemically nickel-plated, LTBC
- Radial offset (μm): 50 μm – 4 μm
At MISUMI, you will find the following linear bearing versions: with locking ring with groove, with dust seal, with lubrication unit (MX), with grease nipple, housing open at the bottom/open, with clearance compensation, with flange, with centred flange, with round flange, with flattened round flange (compact flange), with square flange, with block housing, with wide barrel and ball housing, ball cage guides for linear and rotational movements (limited stroke).
Description/Basics
Linear ball bushings convert the rolling motion of steel balls (4) into infinite linear motion. They can implement highly precise and low-friction linear motion and can be used in almost all industries, e.g., in systems for semiconductor parts, electronic components and in food packaging.
Ball recirculating bushings are used in conjunction with linear shafts. The linear movement mechanism uses steel balls (4) for unlimited linear movement.
Linear bearing units allow linear shafts to travel indefinitely through steel balls that are constantly circulating within the running grooves directed by the outer cylinder and ball cage (3).
Compared to plain bearings, ball bushings perform linear movements with lower friction and high accuracy. They are used in many applications, such as conveyors and semiconductor manufacturing facilities.
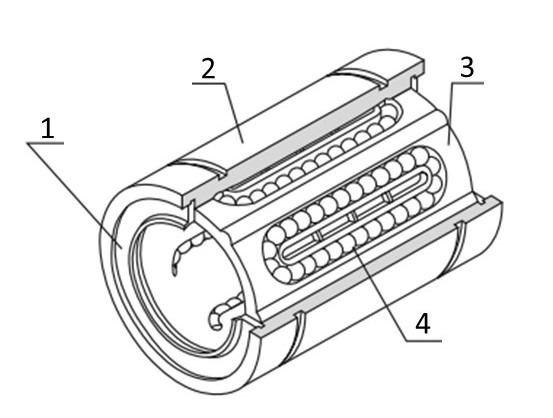
Linear Bearing Unit Design - (1) Dust Seal, (2) Outer Cylinder, (3) Ball Cage, (4) Steel Balls
Dynamic friction coefficient in comparison
| Design | Dynamic friction coefficient (μ) | |
| Miniature profile rail guide | 0.004 ~ 0.006 | |
| Profile rail guide for medium and heavy loads | 0.002 ~ 0.003 | |
| Cross roller guides | 0.001 ~ 0.003 | |
| Cross roller tables | 0.001 ~ 0.003 | |
| Linear ball bearing | 0.002 ~ 0.003 | |
| Ball cage guides | 0.0006 ~ 0.0012 | |
The specified values are for comparison purposes only and are therefore not reference values.
Areas of Application
Linear ball bushings have a linear working direction and can be used for horizontal or vertical linear movements. Therefore, MISUMI linear ball bushings can be used in almost all industries. Since linear ball bushings are intended only for axial movement, rotational use would lead to premature fatigue or destruction of the ball bushings. For rotary movements, we therefore recommend ball cage guides, which enable not only infinite linear movements (stroke-limited) in addition to infinite rotary movements.
Common applications are lifting mechanisms or guides for cylinders. The ball bushings are also a good variant for additional guide. In addition, these linear ball bushings are often found in 3D printers, metering systems, measuring devices, positioning and alignment devices, bending devices and sorting systems.
For systems with increased particle development (e.g., dust and other abrasive particles), the linear systems should be protected with covers or bellows. The ingress of particles leads to a clumping of the lubricating grease or to significantly increased abrasion. By clumping the grease, the balls block in the ball circulation, which results in unscheduled maintenance.
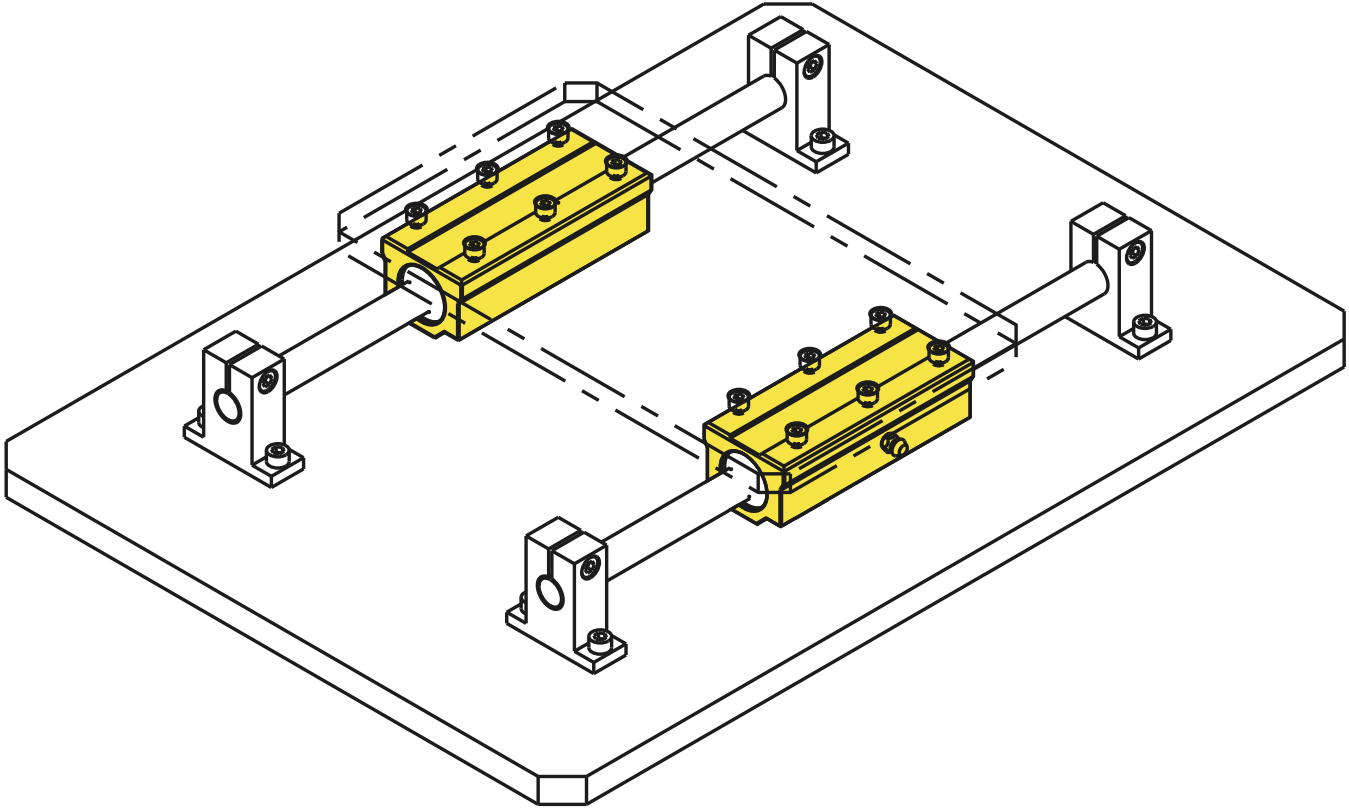
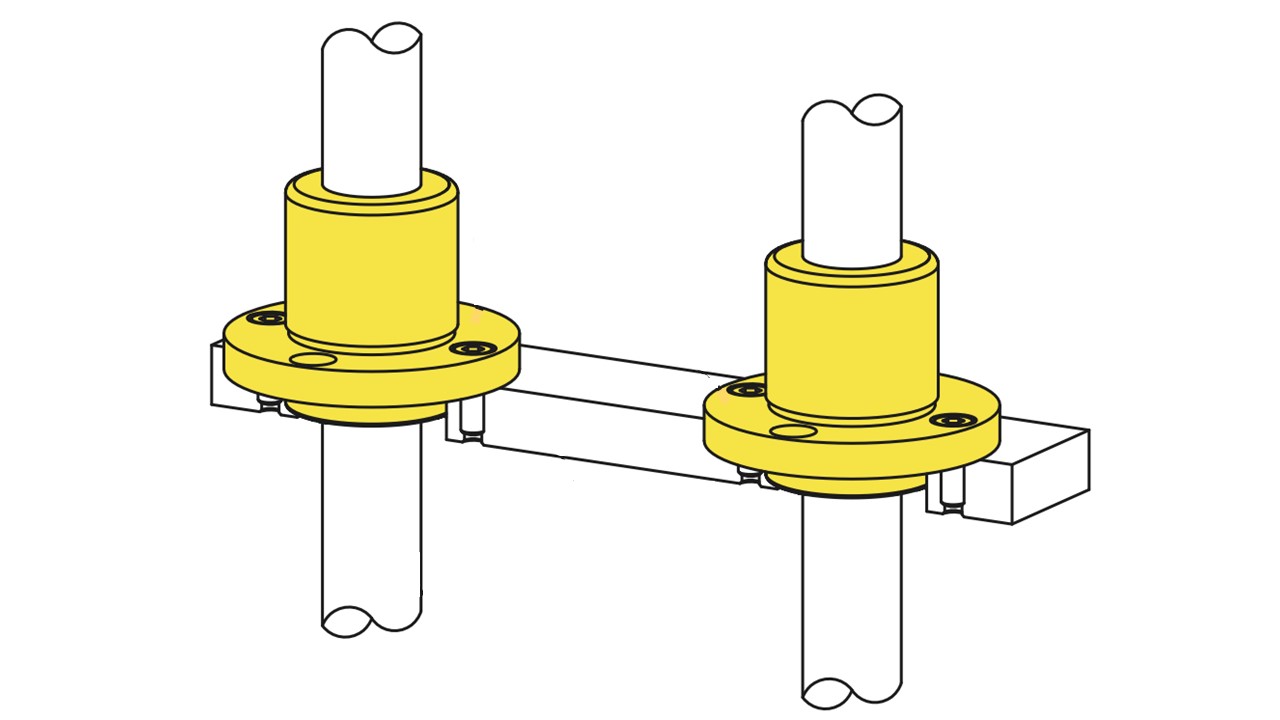
Materials
Linear ball bearings consist of different materials due to their design and the individual components. MISUMI uses high-quality materials to achieve the longest possible service life. The following materials are available:
- External cylinder: stainless steel (stainless steel) ~56HRC, steel with ~58HRC
- Ball: stainless steel (stainless steel), steel
- Ball cage: plastic, stainless steel (stainless steel)
- Housing: aluminum, stainless steel (stainless steel), steel
- Seal: nitrile rubber
You can find more detailed material information in the tab Technical Drawing.
Coatings
To protect linear ball bushings from corrosion, the surface can be chemically nickel-plated.
As an alternative to a chemical nickel-plating, ball bushings can also be coated with LTBC. The LTBC coating (Low Temperature Black Chrome Platinum) is a surface treatment that protects against corrosion and has low reflection. The coating consists of a 5 μm thick chrome ceramic layer with fluoropolymer infusion and it deposits as a black film. In addition, the LTBC coating is crack-proof and interchangeable and is therefore resistant to delamination due to extreme or repeated bending. LTBC-coated linear ball bearings are thus particularly suitable for locations where corrosion or light reflections are undesirable.
Note: the inner wall of LTBC coated linear bushing units is not surface treated.
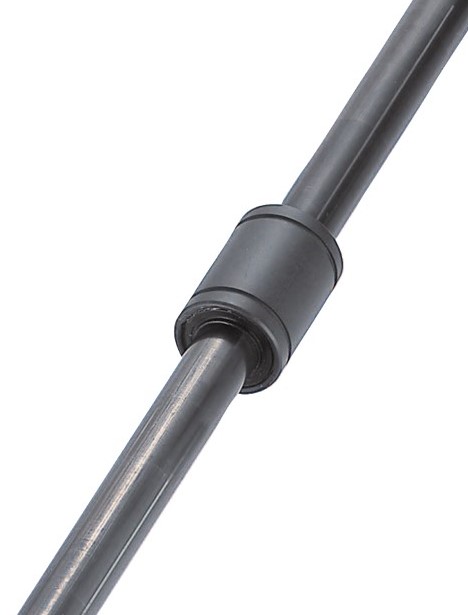

LTBC-coated linear ball bushing - state after 50 km glide test under 412N load.
Comparison test of corrosion protection
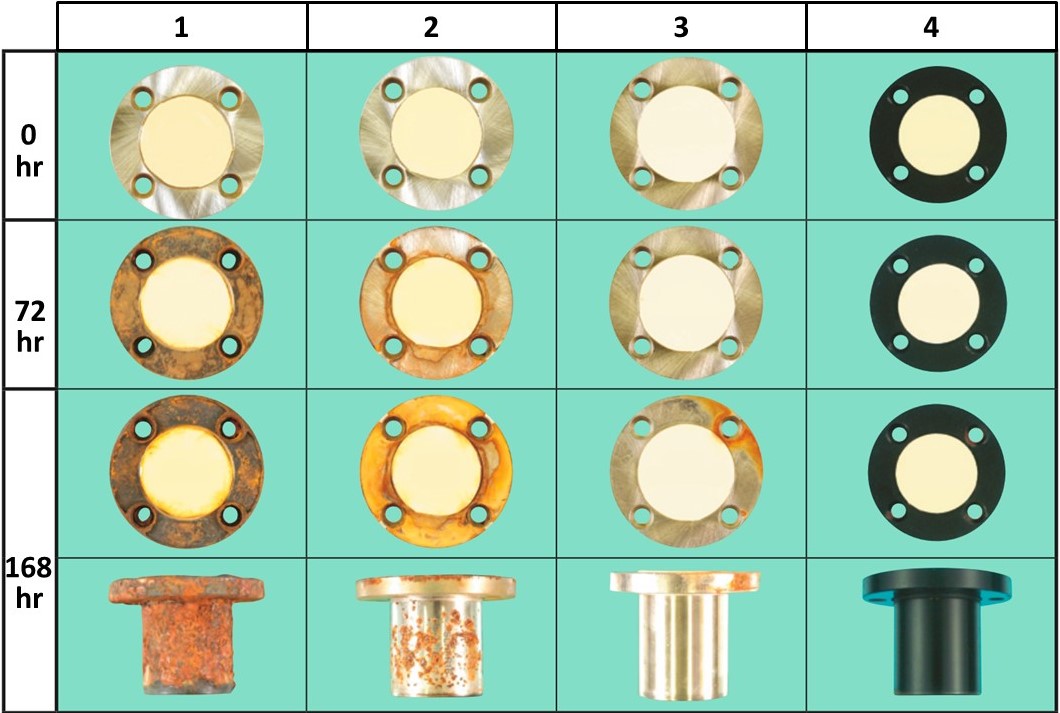
Salt water spray test according to JIS H8502. Test piece: simple flanged linear ball bushing
(1) EN 1.3505 equiv., (2) EN 1.4125 equiv., (3) chemically nickel-plated, (4) LTBC coating, (hr = duration in hours)
Instructions for use
- MISUMI linear bearings should be used in conjunction with MISUMI linear shafts.
- We recommend using a hardened linear shaft in the g6 tolerance.
- An additional hard chrome plating of the linear shaft makes it more wear-resistant.
- When installing ball bushings in housings, we recommend an H7 housing tolerance. Too close a tolerance will reduce the internal contact travel [dr] to the shaft and can lead to increased wear and premature failure.
- The utilisation of two ball bushings on a steel shaft improves the shaft guide in a system. However, if the angular errors are too high, a self-aligning linear ball bushing should be selected.
- When utilising two linear shafts, the drive should be centred in the system to avoid unnecessary stresses/lever effects.
- The service life, also called nominal service life, should be calculated using the present load case. Here you can perform your service life calculation.
- Depending on local conditions such as temperature, humidity and gases, a variant made of stainless steel or an LTBC coating is recommended.
- When the linear shafts bend sharply, a self-aligning/self-adjusting linear ball bushing should be selected.
Installation Information
General installation instructions for linear ball bushings and linear shafts
MISUMI linear ball bushings should be used in conjunction with MISUMI linear shafts (hardened, tolerance g6).
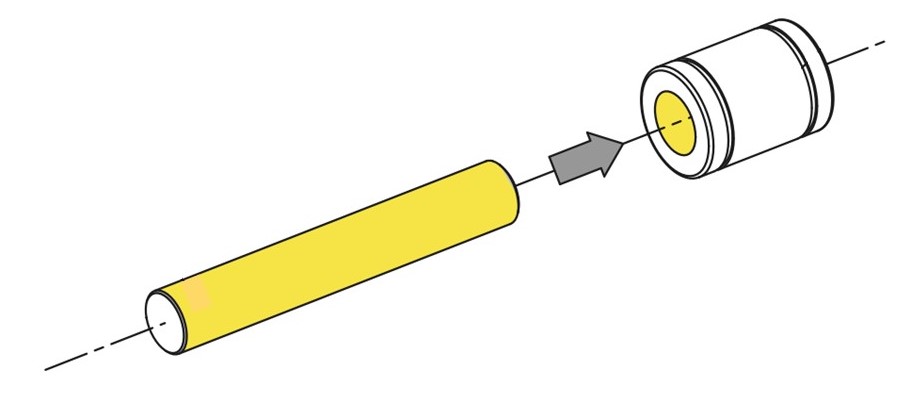
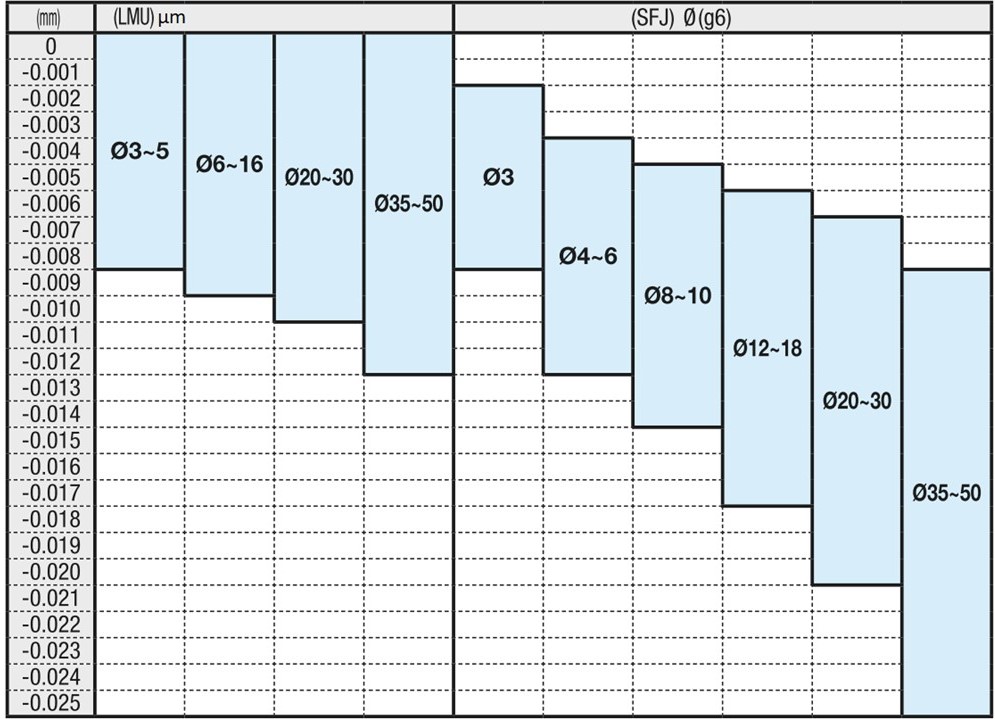
MISUMI tolerance range: inner diameter linear ball bushings (LMU) and outer diameter linear shafts (SFJ).
General installation instructions for linear ball bushings and housings
MISUMI linear ball bushings should be used in conjunction with MISUMI housings (tolerance H7).
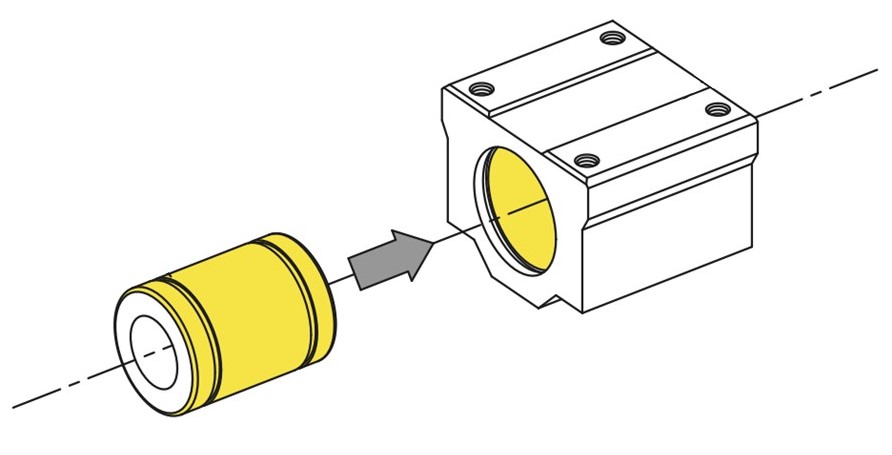
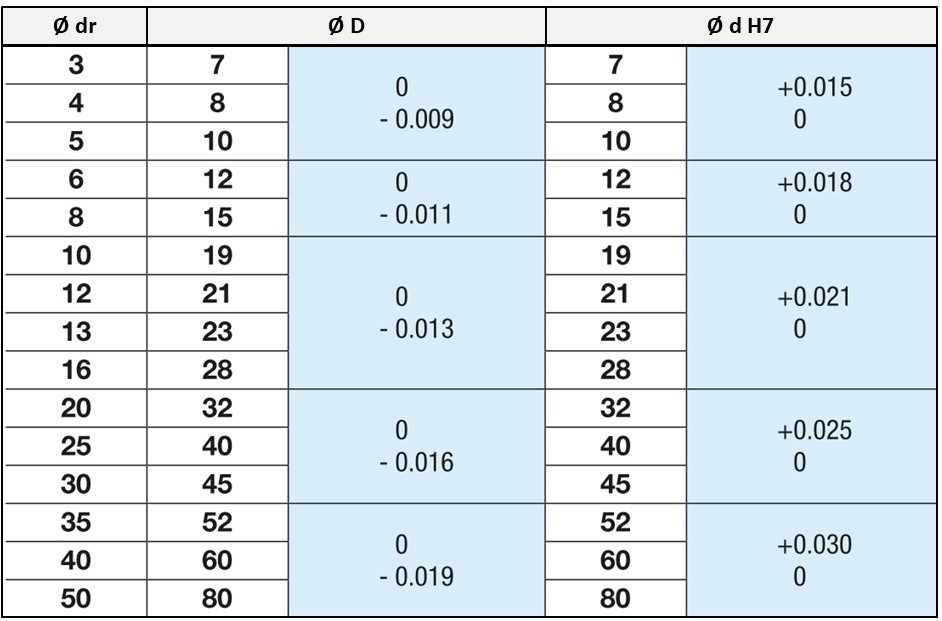
MISUMI tolerance range: outer diameter of linear ball bushing and inner diameter of housing.
Standard linear ball bushing installation instructions
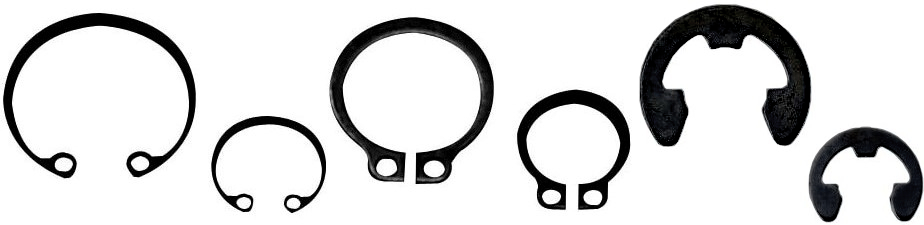
1. When installing standard linear ball bushings, you can use the following locking means: retaining rings (clamping rings), stoppers
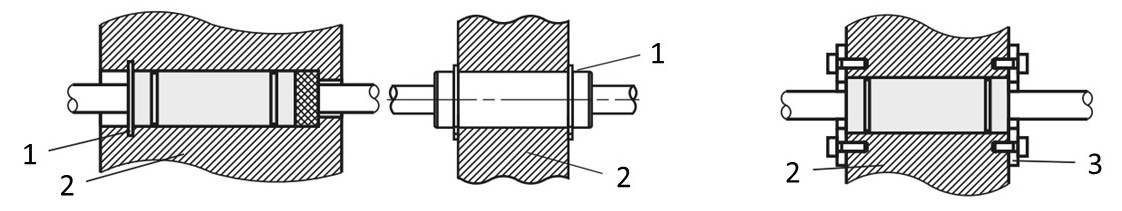
(1) retaining rings, (2) housing, (3) stopper/LMST fixing plate
2. Ball bushings are not suitable for rotary motion and applications requiring repetitive insertion and removal of linear shafts. Such a misuse of the linear ball bushing could damage the recirculating ball bushing.
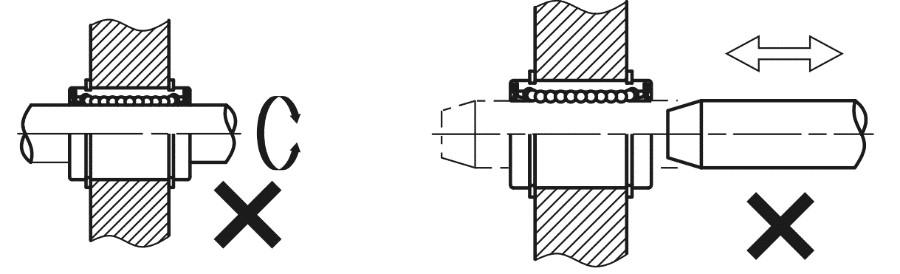
3. Simple linear ball bushings are not suitable for large torque loads (offset load/lever effect). The use of double or multiple linear bushings is recommended for these load cases.
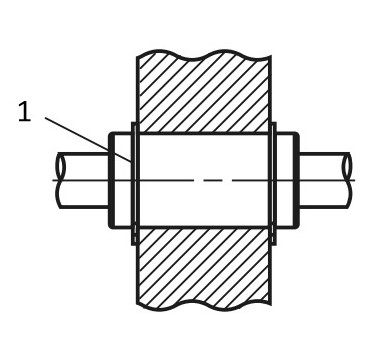
(1) Linear ball bushing with two grooves
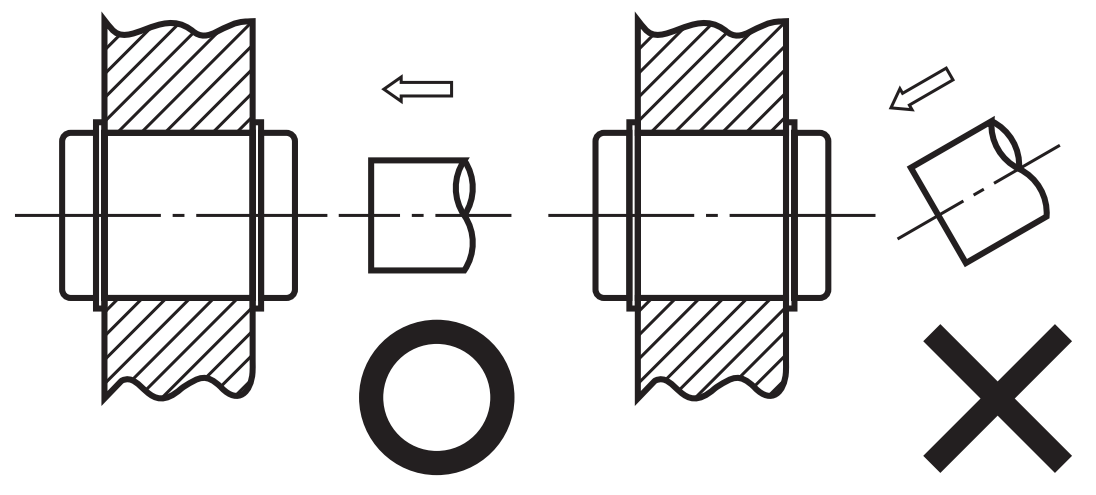
4. When assembling linear shafts, forceful slanted insertion into the linear ball bushing can cause the ball cage to bend and the balls to fall out. Be sure to centre the steel shaft to the linear ball bushing before inserting the steel shaft into the linear ball bushing.
Installation instructions for linear ball bushings with stopper/fixing plate
Through the stopper plates, the versions can be designed independently of the housing length.
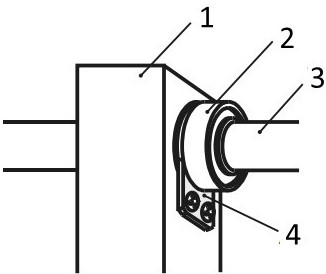
(1) Attachment, (2) linear ball bushing – standard, (3) linear shaft, (4) LMST fixing plate
The stopper plates enable the ball sleeve and linear shaft to be installed flush against the end faces.
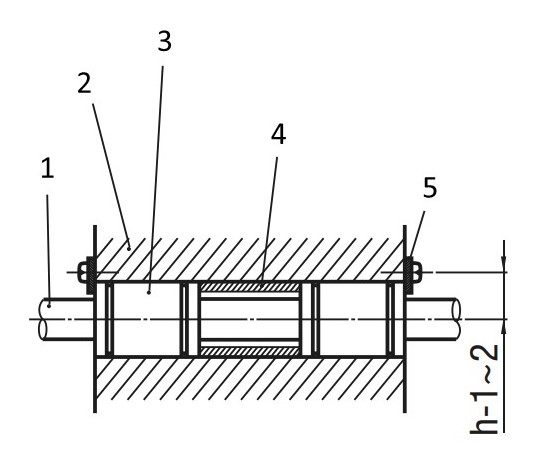
(1) Linear shaft, (2) housing, (3) linear ball bushing – standard, (4) spacer sleeve LBS/LBSA for linear ball bushings, (5) LMST fixing plate
The LMST fixing plates can also be used to lock linear bushings in place.
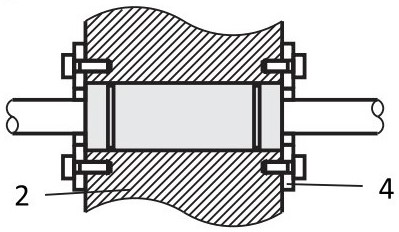
(2) housing, (4) LMST fixing plate
Assembly Instructions for Linear Ball Bushings with Flange and Lubrication Unit MX
When fastening the linear ball bushing with the lubrication unit MX, do not insert the housing of the lubrication unit as guide as shown in (2), as this can damage the housing. Instead, use the flange and guide version as shown in (3).
Do not disassemble the linear ball bushing with flange and lubrication unit MX, as this will impair function.
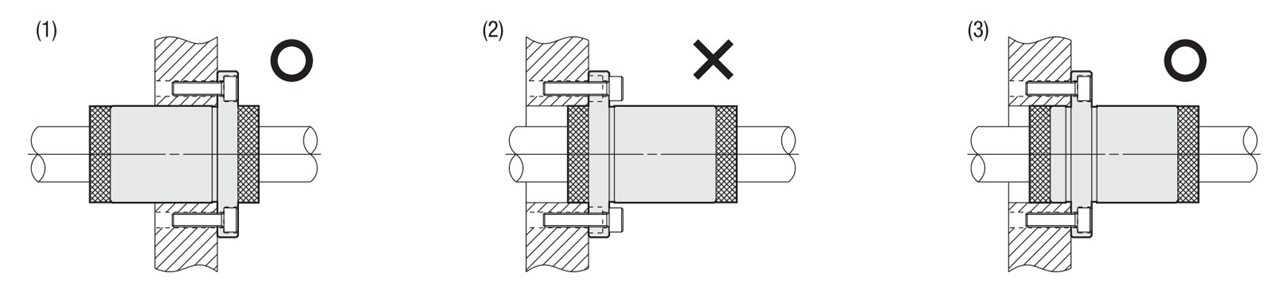
Assembly Instructions for Linear Ball Bushings with Housing and without Cylinder Pin Hole
During interface assembly, centring on the lateral reference surface can be eliminated by means of the cylinder pin holes.
This reduces the machining effort of the upper plate to be mounted on the block.
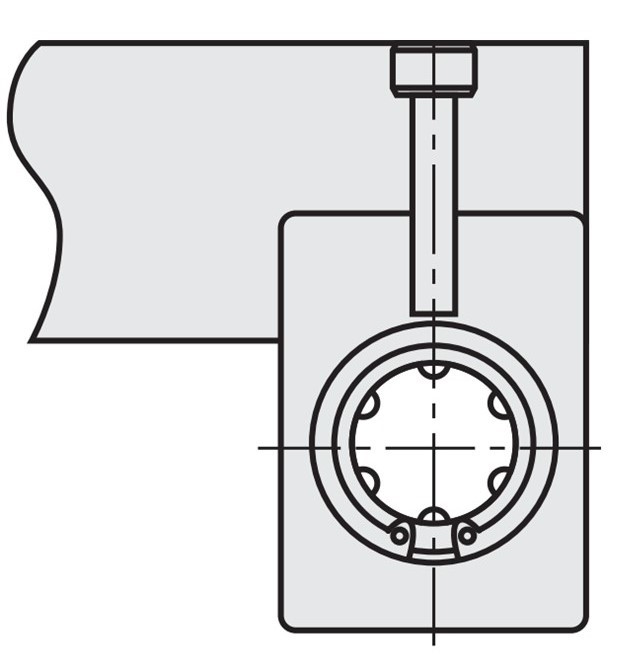
Positioning with plate end cover

Positioning with cylinder pins
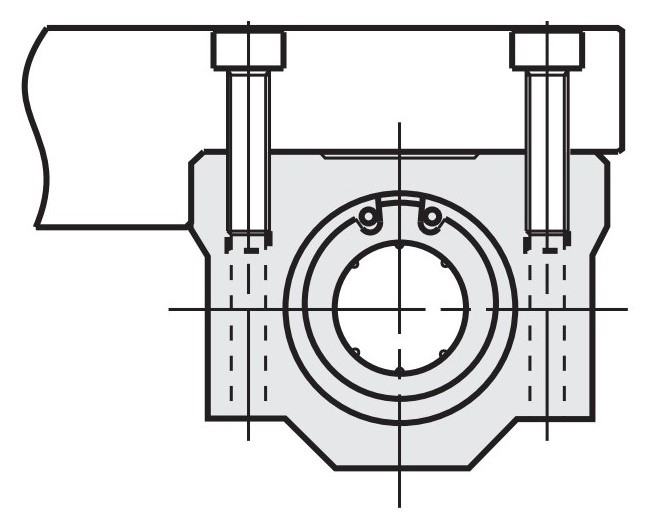
Positioning with plate end cover
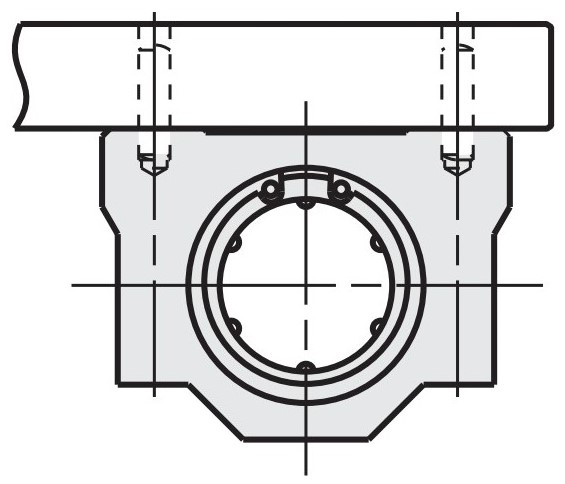
Positioning with cylinder pins
General Maintenance Instructions
Grease the rows of balls inside the ball bushing before use. Then grease regularly during use. Grease reduces friction by forming a layer between the balls and rolling shaft surfaces and prevents seizing. Loss of grease and degradation of grease shorten the service life of linear guides.
- Recommended grease: lithium soap grease
- Recommended lubrication interval: every 6 months
*Every 3 months for extended work or every 1000 km. Maintenance intervals vary depending on the application and ambient conditions.
Lubrication
Linear ball bushings from MISUMI are delivered coated with a corrosion protection oil. Exceptions to this are the designs with lubrication unit MX. After removing the anti-corrosion oil, we recommend lubricating the bearings.
If you select one of the following lubricants in the configurator, you can order pre-lubricated versions. The versions L, G and H are prefilled with grease, whereby L and G offer a strong reduction in particle formation by means of a suitable grease distribution during operation (see quantitative comparison of particle formation below). Lubrication units MX are filled with lithium soap grease.


Assembly of the lubrication unit MX
The lubrication unit MX is equipped with a fibre insert with lubricant. The capillary effect allows the lubricant to be properly applied to contact surfaces. For this purpose, a constant oil film is formed between balls and steel shaft, which significantly prolongs the lubrication intervals.
_cleaned_numbering.jpg)
Recirculation ball bushing with lubrication unit - (1) MX Lubrication Unit, (2) MX Lubrication Unit - Plastic Housing, (3) Lubricant Pads, (4) Dust Seal, (5) Balls, (6) Linear Shaft
Properties of the MX lubrication unit
Longer maintenance intervals: the long-lasting lubricant performance leads to a significant reduction in maintenance, especially in machine and equipment environments where lubrication is difficult to achieve.
Environment: the MX lubrication unit helps reduce lubricant consumption and thus protects the environment.
Cost benefit: it contributes to reducing maintenance costs and failure rate caused by failing to lubricate.
Less effort: it is not necessary to refill the lubricant prior to use, since the ball parts are already filled with a lithium soap-based grease in addition to the lubrication unit.
Comparison test of linear ball bearings and linear ball bearings with lubrication unit
Test conditions:
- Sample: linear ball bushing LMU12 with rust protection oil and linear ball bushing with lubrication unit LMU-MX12
- Effective load: 206N (50% of the dynamic load rating of 412N)
- Average speed: 42 m/min (0.7 m/s)
- Stroke: 100 m
- Lubricant: lubricating grease, only initial filling (only LMU-MX12)
- Shaft material: EN 1.3505 Equiv. (58HRC)
- Duration: 24-hour continuous operation
*The above test conditions serve only as reference values and cannot be considered as a manufacturer warranty.
Test result:
With an effective test load of 50% of the load-carrying capacity of 412N, the design with the MX lubrication unit could achieve a continuous output of 2.5-fold longer than with no MX lubrication unit.
*Since the 2007 catalogue, the data have been updated after the safety limit has been confirmed by further data from test results.
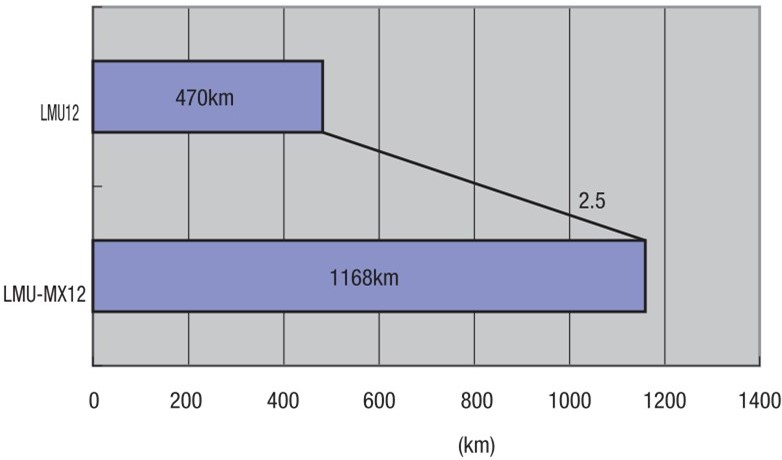
Endurance test result - standard linear ball bearing LMU, linear ball bearing LMU-MX with lubricant unit
_M0101000000.jpg)
_M0103000000_.jpg)
Accessories for Linear Ball Bearing

_M0102000000_.jpg)




Part Number:
- In order to open the 3D preview, the part number must be fixed.
3D preview is not available, because the part number has not yet been determined.
Part Number
|
|---|
| LHSSWF6 |
| Part Number |
Standard Unit Price
| Minimum order quantity | Volume Discount | RoHS | [dr] Inner Diameter (mm) | [L] Length (Total) (mm) | Material of Outer Cylinder | [D] Outer Diameter (mm) | Basic Load Rating Dynamic Rating (Detail) (N) | Basic Load Rating Static Rating (N) | Tolerance of Inscribed Circle (Minus Side) (mm) | Ball Material | Retainer Material | Outer Cylinder Material | Greased filled | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
22.43 € | 1 | Available | 5 Days | 10 | 6 | 46 | [Steel] EN 1.3505 Equiv. | 12 | 324 | 529 | -0.01 | EN 1.4125 Equiv. | Stainless Steel | EN 1.3505 Equiv. | Not Provided |
Loading...
Back to the Category Linear Ball Bushings

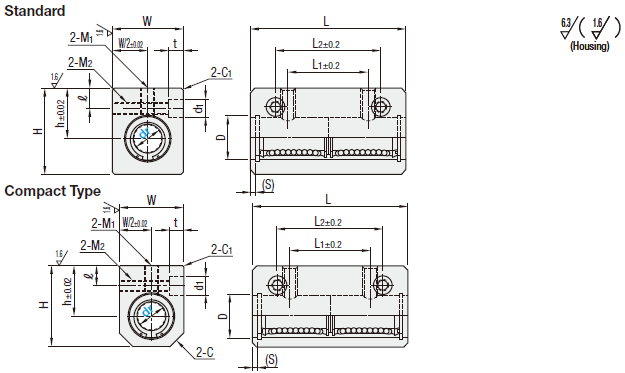
| dr | Tolerance | D | (S) | L | L1 | L2 | h | W | H | ℓ | M1 (Effective Length) | M2 (Effective Length) | C | C1 | d1xt | |||||||
| Standard | Compact | Standard | Compact | Standard | Compact | Standard | Compact | Standard | Compact | Standard | Compact | Standard | Compact | |||||||||
| 4 | 0 -0.008 | 8 | - | 1.1 | 27 | 14 | 22 | 10 | - | 12 | - | 16 | - | 3 | - | M3 (6) | - | M3 (10.5) | - | - | 0.5 | 4.2x1.5 (For M2 Screws) |
| 5 | 10 | - | 4.0 | 40 | 18 | 28 | 13 | - | 15 | - | 20 | - | 5 | - | M4 (8) | - | M4 (10) | - | - | 1 | 6x5 (For M3 Screws) | |
| (6) | 0 -0.010 | 12 | 10 | 3.0 | 46 | 20 | 30 | 14 | 13 | 16 | 14 | 22 | 20 | 4 | M4 (8) | M4 (11) | M4 (9) | 4 | 1 or less | |||
| (8) | 15 | 13 | 56 | 30 | 42 | 16 | 15 | 20 | 17 | 26 | 24 | 5 | M5 (8.5) | M5 (8.5) | M4 (15) | M4 (12) | 5 | 1 or less | ||||
| (10) | 19 | 17 | 4.0 | 68 | 36 | 50 | 19 | 18 | 26 | 23 | 32 | 30 | 6 | 6 | M6 (9.5) | M6 (9.5) | M5 (20) | M5 (17) | 6 | 1 or less | 8x6 (For M4 Screws) | |
| (12) | 21 | 19 | 70 | 20 | 19 | 28 | 25 | 34 | 32 | M5 (22) | M5 (19) | 1 or less | ||||||||||
| 13 | 23 | - | 74 | 42 | 55 | 25 | - | 30 | - | 43 | - | 7 | - | M6 (13) | - | M6 (23) | - | - | 1 | 9x7 (For M5 Screws) | ||
| (16) | 28 | 26 | 3.8 | 84 | 52 | 65 | 27 | 26 | 36 | 33 | 49 | 43 | 7 | M6 (13) | M6 (29) | M6 (26) | 8 | 1 or less | ||||
| 20 | 0 -0.012 | 32 | - | 94 | 58 | 70 | 31 | - | 42 | - | 54 | - | 8 | - | M8 (15) | - | M8 (34) | - | - | 1 | 11x8 (For M6 Screws) | |
| 25 | 40 | - | 3.2 | 128 | 80 | 100 | 37 | - | 52 | - | 65 | - | 9 | - | M10 (17) | - | M10 (42) | - | - | 1 | 14x10 (For M8 Screws) | |
| 30 | 45 | - | 138 | 90 | 110 | 40 | - | 58 | - | 71 | - | - | M10 (17.5) | - | M10 (48) | - | - | 1 | ||||
The datum surface is located on the other side of product ID label.
| dr | Basic Load Rating | Allowable Static Moment (N • m) | Mass (g) | |||||
| C (Dynamic) N | Co (Static) N | Standard | Compact | |||||
| Standard | Compact | Standard | Compact | Standard | Compact | |||
| 4 | 176 | - | 254 | - | 0.63 | - | 14 | - |
| 5 | 263 | - | 412 | - | 1.38 | - | 35 | - |
| 6 | 324 | 206 | 529 | 309 | 2.18 | 2.46 | 40 | 34 |
| 8 | 431 | 383 | 784 | 555 | 4.31 | 5.76 | 75 | 60 |
| 10 | 588 | 585 | 1100 | 867 | 7.24 | 10.99 | 150 | 126 |
| 12 | 657 | 608 | 1200 | 899 | 10.9 | 11.85 | 168 | 150 |
| 13 | 813 | - | 1570 | - | 11.6 | - | 248 | - |
| 16 | 1230 | 965 | 2350 | 1431 | 19.7 | 23.48 | 383 | 296 |
| 20 | 1400 | - | 2740 | - | 26.8 | - | 520 | |
| 25 | 1560 | - | 3140 | - | 43.4 | - | 1120 | - |
| 30 | 2490 | - | 5490 | - | 82.8 | - | 1384 | - |
Basic information
| Type2 | Housings | Style | Standard | Outer Cylinder Surface Treatment | Clear Anodize |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Motion | Linear Motion | Grease Coating | Not Provided | Number of Linear Ball Bearings | Double |
| Accuracy | High-Quality | Type | Pillow Blocks Tall Block Type | Version Length Variant | Double |
| Seals | With Seal |
This page is Linear ball bearings / block form / aluminium / anodised / double bushing, part number LHSSWF6.
You can find the detail information about specifications and dimensions on part number LHSSWF6.
Configure
Basic Attributes
-
Type
- LHSSKW
- LHSSW
- LHSSWF
- SLHSSW
- SLHSSWF
-
[dr] Inner Diameter(mm)
-
[L] Length (Total)(mm)
-
Material of Outer Cylinder
- Steel
- EN 1.4125 Equiv.
- Steel
-
[D] Outer Diameter(mm)
-
Ball Material
- EN 1.3505 Equiv.
- EN 1.4125 Equiv.
-
Retainer Material
- Plastic (POM Equiv.)
- Stainless Steel
-
Outer Cylinder Material
- EN 1.3505 Equiv.
- EN 1.4125 Equiv.
-
Greased filled
- Not Provided
- Type G (Low Particlate)
- Type H (For Food and Beverages)
- Type L (Heat Resistance)
-
Filter by CAD data type
- 2D
- 3D
Filter by standard shipping days
-
- All
- Same day
- 5 Days or Less
- 9 Days or Less
Optional Attributes
- The specifications and dimensions of some parts may not be fully covered. For exact details, refer to manufacturer catalogs .
Variation of this product
| Part Number |
|---|
| LHSSKW10L |
| LHSSKW12 |
| LHSSKW12G |
| LHSSWF6G |
| LHSSWF6H |
| LHSSWF6L |
| Part Number | Standard Unit Price | Minimum order quantity | Volume Discount | Standard Shipping Days ? | RoHS | [dr] Inner Diameter (mm) | [L] Length (Total) (mm) | Material of Outer Cylinder | [D] Outer Diameter (mm) | Basic Load Rating Dynamic Rating (Detail) (N) | Basic Load Rating Static Rating (N) | Tolerance of Inscribed Circle (Minus Side) (mm) | Ball Material | Retainer Material | Outer Cylinder Material | Greased filled |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
42.36 € | 1 | Available | 9 Days | 10 | 10 | 68 | [Steel] EN 1.3505 Equiv. | 17 | 585 | 867 | -0.01 | EN 1.3505 Equiv. | Plastic (POM Equiv.) | EN 1.3505 Equiv. | Type L (Heat Resistance) | |
30.17 € | 1 | Available |
Same day
Stock | 10 | 12 | 70 | [Steel] EN 1.3505 Equiv. | 19 | 608 | 899 | -0.01 | EN 1.3505 Equiv. | Plastic (POM Equiv.) | EN 1.3505 Equiv. | Not Provided | |
50.67 € | 1 | Available | 9 Days | 10 | 12 | 70 | [Steel] EN 1.3505 Equiv. | 19 | 608 | 899 | -0.01 | EN 1.3505 Equiv. | Plastic (POM Equiv.) | EN 1.3505 Equiv. | Type G (Low Particlate) | |
36.10 € | 1 | Available | 9 Days | 10 | 6 | 46 | [Steel] EN 1.3505 Equiv. | 12 | 324 | 529 | -0.01 | EN 1.4125 Equiv. | Stainless Steel | EN 1.3505 Equiv. | Type G (Low Particlate) | |
36.10 € | 1 | Available | 9 Days | 10 | 6 | 46 | [Steel] EN 1.3505 Equiv. | 12 | 324 | 529 | -0.01 | EN 1.4125 Equiv. | Stainless Steel | EN 1.3505 Equiv. | Type H (For Food and Beverages) | |
36.10 € | 1 | Available | 9 Days | 10 | 6 | 46 | [Steel] EN 1.3505 Equiv. | 12 | 324 | 529 | -0.01 | EN 1.4125 Equiv. | Stainless Steel | EN 1.3505 Equiv. | Type L (Heat Resistance) |
Tech Support
- Technical Support
- Tel:+49 69 668173-0 / FAX:+49 69 668173-360
- Technical Inquiry