Screws with collar / hexagon socket with hexagon socket / stepped
Part Number
Once your search is narrowed to one product,
the corresponding part number is displayed here.
- Drawing / Specifications
- 3D Preview 3D preview is available after complete configuration
- Part Numbers
- More Information
- Catalog
Back to the Category Fulcrum Pins
Technical Drawing - Fulcrum Pins

Open the technical drawing in the new window
Available dimensions and tolerances can be found under the tab More information.
Basic Properties (e.g., material, hardness, coating, tolerance) - Fulcrum Pins
| Type | Material | Surface Treatment | Hardness | |
| Standard | Configurable | |||
| CMSG | FCMSG | EN 1.7220 Equiv. | Black Oxide | 33~38HRC |
| SCMSG | FSCMSG | EN 1.4301 Equiv. | - | - |
Further specifications can be found under the tab More information.
Composition of a Product Code - Fulcrum Pins
| Part Number | - | L | - | H | - | F |
| CMSG15 FSCMSG12 | - - | 16 13 | - - | 20.5 8 | - | 10 |
Alterations - Fulcrum Pins

General Information - Fulcrum Pins
.jpg)
Fulcrum Pins Selection Details
- Material: steel, stainless steel
- Coatings: untreated, burnished
- Heat treatment: induction hardened
- Shaft diameter: 4 mm to 20 mm
- Tolerance class of shaft: -0.01mm/+0.05mm, g6
- Thread diameter: M2.6 to M16
- Drive type: hexagon socket, slot, hexagon, key surfaces
Description/Basics
The screwed connection is one of the method most commonly used for detachable connections. Fulcrum pins, also called rotating bolts, have various advantages over conventional screws due to their hardened shaft.
The head of our rotating bolts is in part flatter than that of a stripper bolt, which, in combination with the various drive forms, simplifies the assembly in tight installation spaces. Similar to stripper bolts, Fulcrum pins have a tight-tolerance shaft that can be additionally hardened. This allows designing a simple bearing or guide.
When designing a swivel lock, a combination of Fulcrum pins and links are recommended. This allows, for example, to lock a solid closure. In this case, the rotary bolt can serve both as a bearing point and as an end stop. Its hardened approach offers suitable protection against premature wear in both functions.
Due to the ability to absorb transverse forces and shear forces, bearing bolts with hardened shoulders are suitable for creating a hinge assembly.
Combined with rod end bearings, there is also the option of balancing an offset.
Application Examples - Fulcrum Pins
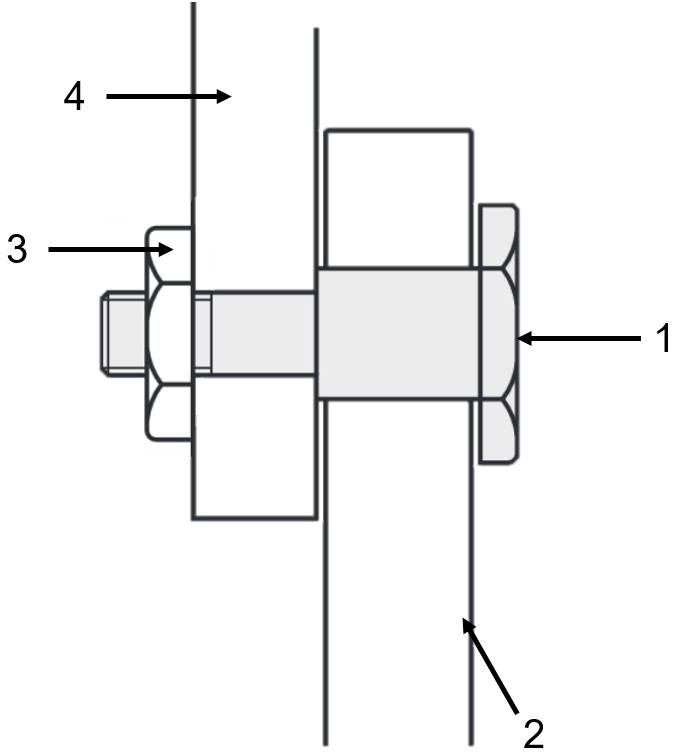
Application example - Fulcrum pin utilised as spacer
1.Fulcrum pin, 2. Flat steel, 3. Nuts , 4. Flat steel

Application Example - Fulcrum pin utilised as bearing point
1.Fulcrum pin, 2. Links, 3. Hex nut, 4. Flat steel

Application example - Fulcrum pin utilised as stopper point
1. Fulcrum pin, 2. Links
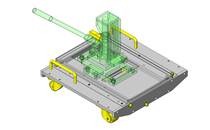
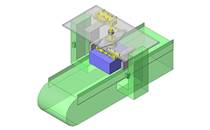
Industrial Applications




Part Number:
- In order to open the 3D preview, the part number must be fixed.
3D preview is not available, because the part number has not yet been determined.
| Part Number | Minimum order quantity | Volume Discount | RoHS | Shaft Dia. D (mm) | Thread Dia. | Material | Hardness | Surface Treatment | Length Configurable | Screw Length F (mm) | Material Detail | Detailed Hardness | H (mm) | L (mm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 Days | 10 | 6 | 4 | EN 1.4301 Equiv. | No Hardened | Not Provided | Length Configurable | 4 ~ 7 | EN 1.4301 Equiv. | No Hardened | 2 ~ 50 | 5 ~ 12 | ||
| 1 | 3 Days | 10 | 8 | 6 | EN 1.4301 Equiv. | No Hardened | Not Provided | Length Configurable | 6 ~ 9 | EN 1.4301 Equiv. | No Hardened | 2 ~ 50 | 5 ~ 16 | ||
| 1 | 3 Days | 10 | 10 | 8 | EN 1.4301 Equiv. | No Hardened | Not Provided | Length Configurable | 8 ~ 12 | EN 1.4301 Equiv. | No Hardened | 3 ~ 70 | 10 ~ 25 | ||
| 1 | 3 Days | 10 | 12 | 8 | EN 1.4301 Equiv. | No Hardened | Not Provided | Length Configurable | 8 ~ 12 | EN 1.4301 Equiv. | No Hardened | 3 ~ 70 | 10 ~ 25 | ||
| 1 | 3 Days | 10 | 13 | 10 | EN 1.4301 Equiv. | No Hardened | Not Provided | Length Configurable | 10 ~ 16 | EN 1.4301 Equiv. | No Hardened | 3 ~ 70 | 10 ~ 25 | ||
| 1 | 3 Days | 10 | 15 | 12 | EN 1.4301 Equiv. | No Hardened | Not Provided | Length Configurable | 12 ~ 18 | EN 1.4301 Equiv. | No Hardened | 4 ~ 80 | 10 ~ 25 | ||
| 1 | 3 Days | 10 | 16 | 12 | EN 1.4301 Equiv. | No Hardened | Not Provided | Length Configurable | 12 ~ 18 | EN 1.4301 Equiv. | No Hardened | 4 ~ 80 | 10 ~ 25 | ||
| 1 | 3 Days | 10 | 18 | 12 | EN 1.4301 Equiv. | No Hardened | Not Provided | Length Configurable | 12 ~ 18 | EN 1.4301 Equiv. | No Hardened | 4 ~ 80 | 10 ~ 25 | ||
| 1 | 3 Days | 10 | 20 | 16 | EN 1.4301 Equiv. | No Hardened | Not Provided | Length Configurable | 16 ~ 24 | EN 1.4301 Equiv. | No Hardened | 4 ~ 100 | 10 ~ 25 | ||
| 1 | 3 Days | 10 | 6 | 4 | EN 1.4301 Equiv. | No Hardened | Not Provided | Length Selection | 7 | EN 1.4301 Equiv. | No Hardened | 2 ~ 50 | 5 ~ 12 | ||
| 1 | 3 Days | 10 | 8 | 6 | EN 1.4301 Equiv. | No Hardened | Not Provided | Length Selection | 9 | EN 1.4301 Equiv. | No Hardened | 2 ~ 50 | 5 ~ 16 | ||
| 1 | 3 Days | 10 | 10 | 8 | EN 1.4301 Equiv. | No Hardened | Not Provided | Length Selection | 12 | EN 1.4301 Equiv. | No Hardened | 3 ~ 70 | 10 ~ 25 | ||
| 1 | 3 Days | 10 | 12 | 8 | EN 1.4301 Equiv. | No Hardened | Not Provided | Length Selection | 12 | EN 1.4301 Equiv. | No Hardened | 3 ~ 70 | 10 ~ 25 | ||
| 1 | 3 Days | 10 | 13 | 10 | EN 1.4301 Equiv. | No Hardened | Not Provided | Length Selection | 16 | EN 1.4301 Equiv. | No Hardened | 3 ~ 70 | 10 ~ 25 | ||
| 1 | 3 Days | 10 | 15 | 12 | EN 1.4301 Equiv. | No Hardened | Not Provided | Length Selection | 18 | EN 1.4301 Equiv. | No Hardened | 4 ~ 80 | 16 ~ 25 | ||
| 1 | 3 Days | 10 | 16 | 12 | EN 1.4301 Equiv. | No Hardened | Not Provided | Length Selection | 18 | EN 1.4301 Equiv. | No Hardened | 4 ~ 80 | 16 ~ 25 | ||
| 1 | 3 Days | 10 | 18 | 12 | EN 1.4301 Equiv. | No Hardened | Not Provided | Length Selection | 18 | EN 1.4301 Equiv. | No Hardened | 4 ~ 80 | 16 ~ 25 | ||
| 1 | 3 Days | 10 | 20 | 16 | EN 1.4301 Equiv. | No Hardened | Not Provided | Length Selection | 24 | EN 1.4301 Equiv. | No Hardened | 4 ~ 100 | 16 ~ 25 |
Loading...
Back to the Category Fulcrum Screws
Technical Drawing - Fulcrum Pins

Open the technical drawing in the new window
Specification Tables - Fulcrum Pins
| D Tolerance | |
| 6 | -0.004 -0.012 |
| 8, 10 | -0.005 -0.014 |
| 12~18 | -0.006 -0.017 |
| 20 | -0.007 -0.020 |
| Part Number | L Selection | H=0.1mm Increment | A | B | C | E | F | MxP (Coarse) | T | Unit Price | ||||||||||
| Type | Dg6 | CMSG | SCMSG | |||||||||||||||||
| CMSG SCMSG | 6 | 5 | 6 | 9 | 10 | 12 | 2.0~ 50.0 | 10 | 3 | 2 | 5 | 7 | 4x0.7 | 6.5 | ||||||
| 8 | 5 | 6 | 9 | 10 | 12 | 16 | 13 | 5 | 3 | 9 | 6x1.0 | 8.7 | ||||||||
| 10 | 10 | 12 | 16 | 19 | 22 | 25 | 3.0~ 70.0 | 17 | 6 | 4 | 12 | 8x1.25 | 10.8 | |||||||
| 12 | 19 | 12.8 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 13 | 8 | 5 | 6 | 16 | 10x1.5 | 14 | ||||||||||||||
| 15 | 16 | 19 | 22 | 25 | 4.0~ 80.0 | 24 | 10 | 6 | 7 | 18 | 12x1.75 | 17 | ||||||||
| 16 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 18 | 27 | 7 | 8 | 19 | ||||||||||||||||
| 20 | 4.0~100.0 | 30 | 14 | 24 | 16x2.0 | 21 | ||||||||||||||
| Part Number | L=1mm Increment | H=0.1mm Increment | F=1mm Increment | A | B | C | E | MxP (Coarse) | T | Unit Price | ||
| Type | Dg6 | FCMSG | FSCMSG | |||||||||
| FCMSG FSCMSG | 6 | 5~12 | 2.0~ 50.0 | 4~ 7 | 10 | 3 | 2 | 5 | 4x0.7 | 6.5 | ||
| 8 | 5~16 | 6~ 9 | 13 | 5 | 3 | 6x1.0 | 8.7 | |||||
| 10 | 10~25 | 3.0~ 70.0 | 8~12 | 17 | 6 | 4 | 8x1.25 | 10.8 | ||||
| 12 | 19 | 12.8 | ||||||||||
| 13 | 10~16 | 8 | 5 | 6 | 10x1.5 | 14 | ||||||
| 15 | 4.0~ 80.0 | 12~18 | 24 | 10 | 6 | 7 | 12x1.75 | 17 | ||||
| 16 | ||||||||||||
| 18 | 27 | 7 | 8 | 19 | ||||||||
| 20 | 4.0~100.0 | 16~24 | 30 | 14 | 16x2.0 | 21 | ||||||
Alterations - Fulcrum Pins

Basic information
| Basic Shape | Hex Socket - Hex Head | Shaft Tolerance | Precision Grade (g6) | Precision | Precision Grade (g6) |
|---|
Configure
Basic Attributes
-
Shaft Dia. D(mm)
-
Thread Dia.
-
Material
- EN 1.7220 Equiv.
- EN 1.4301 Equiv.
-
Surface Treatment
- Black Oxide
- Not Provided
-
Length Configurable
- Length Configurable
- Length Selection
-
Screw Length F(mm)
-
Material Detail
- EN 1.4301 Equiv.
- EN 1.7220 Equiv.
-
Detailed Hardness
- 33 - 38HRC
- No Hardened
-
H(mm)
-
L(mm)
-
Type
- CMSG
- FCMSG
- FSCMSG
- SCMSG
-
Hardness
- Hardened
- No Hardened
-
Filter by CAD data type
- 2D
- 3D
Filter by standard shipping days
-
- All
- 3 Days or Less
- 9 Days or Less
Optional Attributes
- The specifications and dimensions of some parts may not be fully covered. For exact details, refer to manufacturer catalogs .
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Question:
Why do fulcrum pins have a shaft?
-
Answer:
The shank of the fulcrum pin serves primarily as a bearing or pivot point. In addition, the hardened shank can be used as a stopper.
Another advantage may be that the assembly parts can be reduced by using the fulcrum pin with as a spacer.
-
Question:
Are the fulcrum pins offered comparable with the DIN 923?
-
Answer:
In principle, the fulcrum pin and the slotted drive from MISUMI are similar to DIN 923. However, the dimensions differ. For example, the head diameter of the pivot bolt from MISUMI is up to one millimetre larger.
-
Question:
What is the difference between a fitted screw and the socket with pin?
-
Answer:
A fulcrum pin has a less tightly tolerated shank than the shoulder bolts. Therefore, it is more suitable for simpler applications that are less focused on precision. Likewise, the length and diameter of the shank are not freely configurable for all fulcrum pins.
-
Question:
What does the M stand for in the specification of the nominal thread diameter?
-
Answer:
The code letter M indicates that the screw has a metric ISO thread. The metric ISO thread differs fundamentally from standard threads (rough threads) and fine threads. Assembly parts equipped with an M-thread and the same thread size are compatible with each other (example: M8 screw/M8 nut).
Complementary Products
MISUMI Unit еxample related to this product
Tech Support
- Technical Support
- Tel:+49 69 668173-0 / FAX:+49 69 668173-360
- Technical Inquiry