Miniature profiled rail guides (Part Numbers - CAD Download)
- Volume Discount
- Lead Time Reduction
- Order quantities extended (D-JIT)
Part Number
Once your search is narrowed to one product,
the corresponding part number is displayed here.
- Drawing / Specifications
- 3D Preview 3D preview is available after complete configuration
- Part Numbers
- More Information
- Catalog
- Technical Information
Back to the Category Linear Rail Guides / Profile Rail Guides
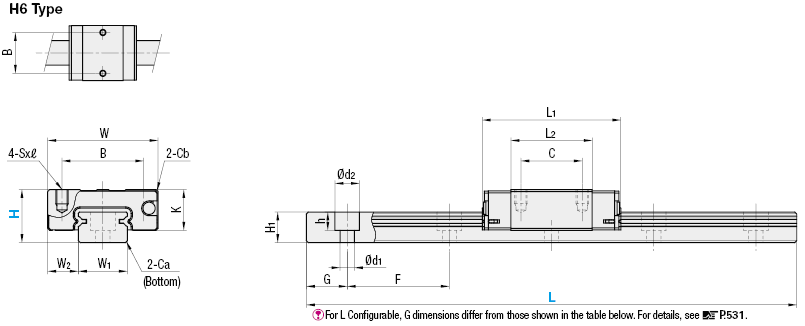
Available dimensions and tolerances can be found under the tab More Information .
| Material Hardness | Type | MX (Lubrication Unit) | L Dimension | Number of Blocks | ||
| Light Preload | Slight Clearance | |||||
| High Grade | Precision Grade | Standard Grade | ||||
| Stainless Steel 56HRC~ | SSEB | SSEBV | SSEBZ | Blank: None -MX: Provided | Selectable | 1 |
| SSE2B | SSE2BV | SSE2BZ | 2 | |||
| SSEBL | SSEBLV | SSEBLZ | Configurable | 1 | ||
| SSE2BL | SSE2BLV | SSE2BLZ | 2 | |||
Basic height 6 (H6) is only available for the types SSEB, SSE2B, SSEBL, SSE2BL.
Further specifications can be found under the tab More Information .
Blocks are equipped with retainers (wire) to prevent balls from falling off.
For how to handle the blocks, see >>P.525.
Radial clearances and accuracies are not guaranteed if the blocks and rails are interchanged from the original set combinations.
Straight grooves are provided on datum planes.
Be sure to match the datum lines when using.
Rails cannot be connected end to end.
The accuracy of Linear Guides is guaranteed after mounting the rail (after fastening screws on the rail and pushing it onto the datum plane).
Minor bending of the rail will be adjusted after being mounted and will not affect the performance.
■Accessory
• H6 comes with Number 0, Class 1 Phillips button head screws (M2x6).
• H8 comes with cap screws (M2x6).
■Others
• Filled with Lithium soap based grease (Multemp Grease PS2 by Kyodo Yushi Co., Ltd. ).
• For operating life calculation, see >>P.527.
• For operating life calculations, use our free calculation software from http://download.misumi.jp/mol/fa_soft.html.
• The MX type is greased with a lithium complex grease (TOUGHLIX GREASE MP2, made by JXTG Nippon Oil & Energy Corporation).
| Part Number | - | L | |
| SSEB10 SSEB-MX10  RSEB10 RSEB10 SSEB10L SSEB10L SSEB10G SSEB10G | - - - - - | 275 275 75 75 75 | (With Lubrication Unit) (LTBC Plating) (L Type Greased) (G Type Greased) |
>> P.531

Here to the Overview of Options as PDF.

Selection details of profile rail guides with rolling elements
- Material: steel, stainless steel
- Coatings: uncoated, LTBC coated
- Hardness: up to ~58HRC
- Precision classes: standard class, high quality, precision class
- Mounting height: 6 mm to 45 mm
- Guide rail width: 5 mm to 42 mm
- Guide rail length: 25 mm to 1960 mm
- Pretension: slight play, slight pretension
- Guide carriage versions: short, wide, wide and long, long, extra long
Description/Basics
A profile rail guide is a commonly used rolling linear guide in mechanical engineering.
The advantages of this linear guide are its rigidity, carrying capacity, running accuracy and precision. The ball-bearing guide carriage (block/carriage) allows a limitless stroke over the length of the linear guide rail. Compared to linear guides guided against rollers, the balls in the guide carriage enable the achievement of high speeds.
The linear guide rail and guide carriage are precisely coordinated and enable a high running accuracy for highly precise applications. It is therefore recommended purchasing the profile rail guide as a set for precise applications, as these are tested together for accuracy and precision.
The profile rails are available in the MISUMI online shop in standardized lengths or configurable in 1 mm increments. The various additional options expand the versatility and possible applications.
Useful Life
After determining the permissible load, the useful life of a profile rail guide must be calculated depending on the application. This not only depends on the applied load, torque and lubrication, but also on many other factors. In the following link you will find the useful life calculation and design of profile rail guides.
Note: MISUMI linear guides are coated with lubricants to protect them from oxidation during transport.
Maintenance
Lubricate the linear guide/lubrication intervals
To reduce friction and wear, linear guides such as the profile rail guides should be lubricated regularly. The lubrication interval varies depending on the application and ambient condition, as this depends on many factors. The general recommended lubrication intervals of the profile rail guides are in the range of approx. 6 months. For long strokes, the lubrication intervals are reduced to approx. 3 months or every 1000 km. Here, too, it is recommended to check the lubrication performance initially at shorter intervals and to adjust it to the existing operating conditions. Too much lubricant should not be introduced into the linear guide, as too much lubricant can lead to increased resistance and damage.
For smaller profile rail guides, such as miniature linear guides, the linear guide can be lubricated over the linear rail. For this purpose, the lubricant can be applied to the running surfaces of the linear rail.
Structurally larger profile rail guides have a grease nipple to get the lubricant to the necessary areas.
Alternative lubricants
The MISUMI linear guides are pre-greased with the lubricant. As a standard, the profile rail guides are filled with lithium soap grease. The Multemp lubricant PS2 (from Kyodo Yushi Co. Ltd) is applied in the miniature profile rail guides. Profile rail guides for medium and heavy loads are pre-greased with Alvania Grease S2 (from Showa Shell Sekiyu K.K.). Alternatively, an alternative grease filling may be selected for the linear guide. For this purpose, a heat-resistant grease (L) and cleanroom-compatible grease (G) are available.
Lubricant | Designation | Property |
L | ET-100K (Kyodo Yushi) | Heat and oxidation resistance, as well as high adhesion and cohesion strength. Low spray and leak probability |
G | LG2 (NSK Ltd.) | Cleanroom-compatible special lubricant for linear guides, ball screw, etc. |
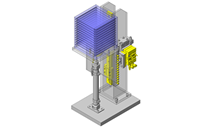
Lubrication unit (MX)
Another variant is the profile rail guide with lubrication unit (MX). The lubrication unit extends the lubrication intervals by supplying lubricant at the ends of the linear guide carriage. This means that not only the lubrication effort, but also the maintenance costs, can be reduced. The lubrication units are filled with lithium soap grease as standard.
.jpg)
Profile rail guide with lubrication unit (MX)
Function

(1) Dust seal, (2) ball circulation, (3) guide carriage, (4) profile rail, (5) ball cage (wire), (6) ball
In principle, the profile rail guide is provided with a ball bearing, which guides the balls back to the profile rail in a circular manner during the movement loop (closed system). As a result, this linear guide is not subject to any real stroke limit, except for the length of the guide rail used. The compact miniature profile rail guides have two ball revolving movements, the balls of which have contact at four points for the load suspension. Heavy duty and medium duty linear guides have four ball recirculations, each with contact at two points in X or O alignment. Lateral seals prevent dirt particles from penetrating, which protect the balls from heavy wear. A wire (ball cage) within the guide carriage makes it difficult for balls to fall out. This is essential for the function of the linear guide.
Areas of Application
MISUMI profile rail guides can be used in almost all linear movement applications.
As opposed to other linear systems, the profile rail guide can absorb moments in different directions. This ensures rigidity in an application. Precision and running accuracy ensure precise guidance and movement. The profile rail guide can often be found in 3D printers, hoisting mechanisms, measuring devices, and positioning jigs. The linear guide is often used in conjunction with ball screw to achieve high positioning accuracy. MISUMI offers an additional option for the profile rail guide for parallel use [WC ], which sets the height difference to 15 μm under the rail pair.
The compact design also allows these linear guides to be used in confined spaces.
Materials
The MISUMI miniature rail guides are available in stainless steel. Heavy-duty and medium-duty linear guides can be configured in steel and stainless steel.
Coatings
The profile rail guides are uncoated and available with an LTBC plating. The LTBC plating consists of a durable anodized fluoropolymer layer applied to the linear rail and guide carriage. It is resistant to flaking and offers good protection against corrosion.
Dimensions
Precision standards
The precision standards such as standard class, high quality and precision class describe the dimensional manufacturing accuracy of the linear guides. More detailed information can be found under the tab Additional Information
Information about running parallelism and dimensional accuracy can be found in this link.
Instructions for use
Since the ball loop is completely run through in a certain stroke length, continuous short strokes are not recommended due to the distribution of the lubricant. With short strokes of the guide carriage, punctual wear may occur on the linear guide rail and balls as well as the linear guide can fail. In order for the lubricant to distribute evenly, sufficient stroke should be ensured when using a profile rail guide.
The profile rail guides can be used in all orientations (levels). When replacing a guide carriage with a new one, it is recommended that the guide carriage be pushed against the profile rail carefully against the transport rail end. For pre-stressed linear guides, the removal of the guide carriage is generally not recommended, since balls can fall out of the guide carriage when reassembled.
It should be noted that the profile rail guide should not bump. This may damage the balls in the guide carriage, impair function and ultimately lead to component failure.

In general, it is not recommended to remove the guide carriage from the profile rail. If the guide carriage has to be removed from the guide rail, it is recommended to reverse the profile rail guide. This reduces the risk of balls falling should become loose. Slowly push the guide carriage (sled) off the profile rail. When replacing the guide carriage, push the profile rail straight and carefully into the guide carriage. If the linear rail is inserted at an angle, balls can fall out of the guide carriage and damage the plastic cage.

Installation Information
Reference surface of the profile rail guide
In general, it is not recommended to remove the guide carriage from the profile rail. If the guide carriage has to be removed from the guide rail, it is recommended to reverse the profile rail guide. This reduces the risk of balls falling should become loose. Slowly push the guide carriage (sled) off the profile rail. When replacing the guide carriage, push the profile rail straight and carefully into the guide carriage. If the linear rail is inserted at an angle, balls can fall out of the guide carriage and damage the plastic cage.
Miniature linear guide | Medium and heavy duty linear guide | ||
Standard and C-value | Standard linear guide | Standard with plastic ball cage | C-value |
|
|
|
|
The MISUMI profile rail guides are provided with reference surface markings for assembly. These are used for the alignment of the linear guides and as an indicator for the precisely manufactured reference surfaces. The reference surfaces serve as a reference for the contact surface of the base plate for the linear guide rail. Prior to assembly, the respective contact surfaces of the profile rail and base plate should be cleaned of any contamination.
Fixation of the linear guide rail and guide carriage

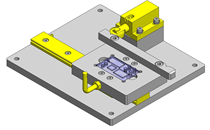
(1) Assembly with pusher plates, (2) assembly with tapered machine keys, (3) assembly with rail pusher plates
For high precision applications and applications for loads as well as vibrations and impact, additional clamping against the reference surface is recommended. This can be achieved with pusher plates (1) on the guide carriage and guide rail. Another variant is clamping via tapered machine keys (2), which hold the linear rail and linear guide carriage in position via a spreading process. For long guide rails, rail pusher plates (3), which clamp and hold the profile rail to the reference surface of the base plate.
For more information, see the Installation and Maintenance available as PDF
Adjustment without base plate stopper
- Position the profile rail on the base plate and fasten it temporarily with the screws (Fig. 1)
- Place ruler with dial gauge parallel to linear rail.
- Hand-tighten screws and perform the measuring process with the dial gauge and set parallelism.
- Tighten screws to the recommended torque and fasten profile rail.
- Like the first linear rail, the second linear rail can be adjusted using a ruler. However, the probability of high parallelism increases when the dial gauge is attached to the already mounted profile rail for measurement and adjustment. (Fig. 2)

(1) Adjustment of first profile rail guide, (2) adjustment of second profile rail guide
For more information, see the Installation and Maintenance available as PDF

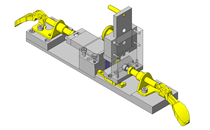
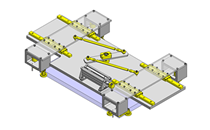
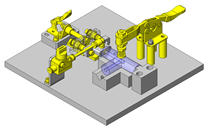
Application example – linear guide as hoisting device with crank
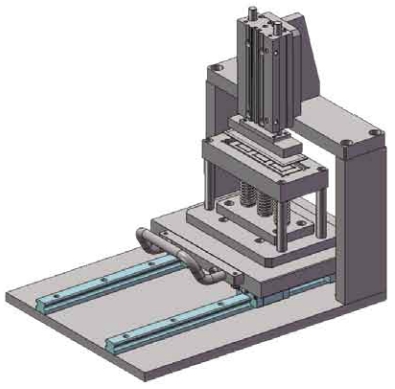
Application example – linear guide press

Application example - positioning with air cylinder

Application example – profile rail guide as XY coordinate stage

Application example – linear guide with gripper

Application example – profile rail guide with timing belt

_-_Sortiment.jpg)

Dowel pins/spring pins/stepped pins

Profile rail guide (special versions)
_-_Sortiment.jpg)




Part Number:
- In order to open the 3D preview, the part number must be fixed.
3D preview is not available, because the part number has not yet been determined.
Part Number
|
|---|
| SSEBZ13G-470 |
| SSEBZ13L-470 |
| SSEBZ16-470 |
| SSEBZ16G-470 |
| SSEBZ16L-470 |
| SSEBZ-MX13-470 |
| SSEBZ-MX16-470 |
| Part Number |
Standard Unit Price
| Minimum order quantity | Volume Discount | RoHS | Rail Width W1 (mm) | Assembly Height H (mm) | No. of Blocks | Rail Length L (mm) | Preload | Accuracy Standards | Nominal Part Number | Lubrication Type | Basic Load Rating: Dynamic Load (N) | Basic Load Rating: Static Load (N) | Allowable Static Moment MA (Nm) | Allowable Static Moment MB (Nm) | Allowable Static Moment MC (Nm) | Grease Type | L Dimension Type | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
- | 1 | 7 Days | 10 | 12 | 13 | 1 | 470 | [Clearance] Interchangeable, Slight Clearance | Standard Grade | 12 | - | 2200 | 3300 | 8.8 | 9.5 | 16.1 | Low Dust Generation Grease (G Type) | Selectable Type | ||
- | 1 | 7 Days | 10 | 12 | 13 | 1 | 470 | [Clearance] Interchangeable, Slight Clearance | Standard Grade | 12 | - | 2200 | 3300 | 8.8 | 9.5 | 16.1 | Heat Resistant Grease (L Type) | Selectable Type | ||
- | 1 | 7 Days | 10 | 15 | 16 | 1 | 470 | [Clearance] Interchangeable, Slight Clearance | Standard Grade | 15 | - | 3600 | 5400 | 21.6 | 23.4 | 39.6 | Lithium Soap Base Grease filled | Selectable Type | ||
- | 1 | 7 Days | 10 | 15 | 16 | 1 | 470 | [Clearance] Interchangeable, Slight Clearance | Standard Grade | 15 | - | 3600 | 5400 | 21.6 | 23.4 | 39.6 | Low Dust Generation Grease (G Type) | Selectable Type | ||
- | 1 | 7 Days | 10 | 15 | 16 | 1 | 470 | [Clearance] Interchangeable, Slight Clearance | Standard Grade | 15 | - | 3600 | 5400 | 21.6 | 23.4 | 39.6 | Heat Resistant Grease (L Type) | Selectable Type | ||
- | 1 | 8 Days | 10 | 12 | 13 | 1 | 470 | [Clearance] Interchangeable, Slight Clearance | Standard Grade | 12 | Lubrication Applied | 2200 | 3300 | 8.8 | 9.5 | 16.1 | Lubrication Units | Selectable Type | ||
- | 1 | 8 Days | 10 | 15 | 16 | 1 | 470 | [Clearance] Interchangeable, Slight Clearance | Standard Grade | 15 | Lubrication Applied | 3600 | 5400 | 21.6 | 23.4 | 39.6 | Lubrication Units | Selectable Type |
Loading...
Back to the Category Linear Rail Guides / Profile Rail Guides

| Part Number | L | Block Dimension | Guide Rail Dimension | |||||||||||||||||
| Type | MX | H | W | L1 | B | C | Sxℓ | L2 | K | Cb | W1 | W2 | H1 | Ca | Counterbored Hole | F | G | |||
| d1xd2xh | ||||||||||||||||||||
| SSEB SSE2B SSEBL SSE2BL | SSEBV SSE2BV SSEBLV SSE2BLV | SSEBZ SSE2BZ SSEBLZ SSE2BLZ | - | 6 | 25~100 (70) | 12 | 17.4 | 8 | - | M2x1.5 | 9.7 | 4.5 | 0.3 | 5 | 3.5 | 4 | 0.3 | 2.4x3.5x1 | 15 | 5 |
| 8 | 40~130 (70) | 17 | 23.6 | 12 | 8 | M2x2.5 | 13.6 | 6.5 | 0.3 | 7 | 5 | 4.7 | 0.3 | 2.4x4.2x2.3 | 15 | 5 | ||||
| Blank: None -MX: Provided | 10 | 35~275 (75) | 20 | 30 | 15 | 10 | M3x3 | 19 | 7.8 | 0.3 | 9 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 0.3 | 3.5x6x3.5 | 20 | 7.5 | |||
| 13 | 45~470 (95) | 27 | 33.9 | 20 | 15 | M3x3.5 | 19.9 | 10 | 0.5 | 12 | 7.5 | 7.5 | 0.5 | 3.5x6x4.5 | 25 | 10 | ||||
| 16 | 70~670 (110) | 32 | 42.4 | 25 | 20 | M3x4 | 27.4 | 12 | 0.5 | 15 | 8.5 | 9.5 | 0.5 | 3.5x6x4.5 | 40 | 15 | ||||
| Dimensions in ( ) are for 2-Block Type. | 20 | 100~700 (160) | 40 | 50 | 30 | 25 | M4x6 | 34.6 | 15 | 0.5 | 20 | 10 | 11 | 0.5 | 6x9.5x5.5 | 60 | 20 | |||
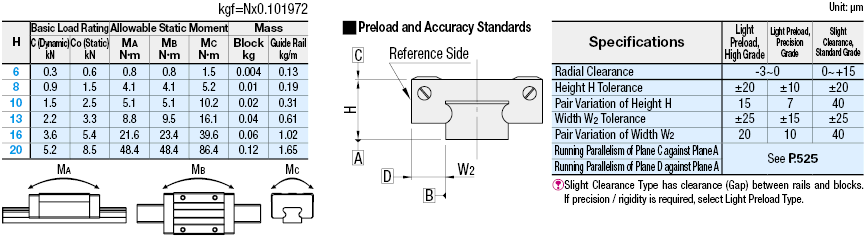

Blocks are equipped with retainers (wire) to prevent balls from falling off.
For how to handle the blocks, see >>P.525.
Radial clearances and accuracies are not guaranteed if the blocks and rails are interchanged from the original set combinations.
Straight grooves are provided on datum planes.
Be sure to match the datum lines when using.
Rails cannot be connected end to end.
The accuracy of Linear Guides is guaranteed after mounting the rail (after fastening screws on the rail and pushing it onto the datum plane).
Minor bending of the rail will be adjusted after being mounted and will not affect the performance.
■Accessory
• H6 comes with Number 0, Class 1 Phillips button head screws (M2x6).
• H8 comes with cap screws (M2x6).
■Others
• Filled with Lithium soap based grease (Multemp Grease PS2 by Kyodo Yushi Co., Ltd. ).
• For operating life calculation, see >>P.527.
• For operating life calculations, use our free calculation software from http://download.misumi.jp/mol/fa_soft.html.
• The MX type is greased with a lithium complex grease (TOUGHLIX GREASE MP2, made by JXTG Nippon Oil & Energy Corporation).
Basic information
| Set / Single Item | Set | Block Type | Standard Block | Rail Type | Standard Rail |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material | Stainless Steel | Ball Arrangement | Miniature Type | Retainer | Not Provided |
| Rolling Element | Balls |
Configure
Basic Attributes
-
Rail Width W1(mm)
-
Assembly Height H(mm)
-
No. of Blocks
- 1
- 2
-
Preload
- Light Preload
- Clearance
- Light Preload
-
Accuracy Standards
- Standard Grade
- High Grade
- Precision Grade
-
Nominal Part Number
-
Lubrication Type
- Lubrication Applied
-
Grease Type
- Heat Resistant Grease (L Type)
- Lithium Soap Base Grease filled
- Low Dust Generation Grease (G Type)
- Lubrication Units
-
L Dimension Type
- Configurable Type
- Selectable Type
-
Type
- SSE2B
- SSE2B-MX
- SSE2BL
- SSE2BL-MX
- SSE2BLV
- SSE2BLV-MX
- SSE2BLZ
- SSE2BLZ-MX
- SSE2BV
- SSE2BV-MX
- SSE2BZ
- SSE2BZ-MX
- SSEB
- SSEB-MX
- SSEBL
- SSEBL-MX
- SSEBLV
- SSEBLV-MX
- SSEBLZ
- SSEBLZ-MX
- SSEBV
- SSEBV-MX
- SSEBZ
- SSEBZ-MX
-
Rail Length L(mm)
- 25
- 35
- 40
- 45
- 55
- 70
- 75
- 85
- 95
- 100
- 110
- 115
- 120
- 130
- 135
- 145
- 150
- 155
- 160
- 170
- 175
- 190
- 195
- 205
- 215
- 220
- 230
- 235
- 245
- 250
- 255
- 265
- 270
- 275
- 280
- 295
- 310
- 315
- 320
- 335
- 340
- 345
- 350
- 355
- 370
- 375
- 390
- 395
- 400
- 415
- 420
- 430
- 435
- 445
- 455
- 460
- 470
- 475
- 495
- 510
- 515
- 520
- 535
- 545
- 550
- 555
- 570
- 575
- 580
- 590
- 595
- 615
- 620
- 630
- 635
- 640
- 645
- 670
- 695
- 700
- 710
- 720
- 745
- 750
- 760
- 770
- 790
- 795
- 820
- 830
- 845
- 870
- 880
- 895
- 910
- 920
- 940
- 945
- 950
- 970
- 990
- 1000
[26-989/1mm Unit(s)]
-
Filter by CAD data type
- 2D
- 3D
Filter by standard shipping days
-
- All
- 7 Days or Less
- 8 Days or Less
Optional Attributes
- The specifications and dimensions of some parts may not be fully covered. For exact details, refer to manufacturer catalogs .
Tech Support
- Technical Support
- Tel:+49 69 668173-0 / FAX:+49 69 668173-360
- Technical Inquiry